Polymer networks with bicontinuous gradient morphologies resulting from the competition between phase separation and photopolymerization†
Abstract
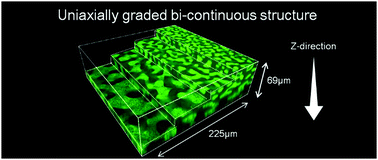
Poly(ethyl acrylate)/poly(methyl methacrylate) (PEA/PMMA) polymer networks (IPNs) with spatially graded bicontinuous morphology were designed and controlled by taking advantage of the spinodal decomposition process induced by photopolymerization of the MMA monomer. Spatial gradients of the quench depth, induced by the gradients of light intensity, were generated along the path of the excitation light travelling through the mixture. Bicontinuous structures with uniaxial gradient of characteristic length scales were obtained by two different methods: simply irradiating the mixture with strong light intensity along the Z-direction and using the so-called computer-assisted irradiation (CAI) method with moderate intensity to generate the light intensity gradient exclusively in the XY plane. These experimental results suggest that the combination of these two irradiation methods could provide polymer materials with biaxially co-continuous gradient morphology. An analysis method using the concept of spatial correlation function was developed to analyze the time-evolution of these graded structures. The experimental results obtained in this study suggest a promising method to design gradient polymers in the bulk state (3D) as well as on the surface (2D) by taking advantage of photopolymerization.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...