Anisotropic reversible piezoresistivity in magnetic–metallic/polymer structured elastomeric composites: modelling and experiments
Abstract
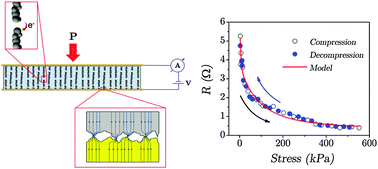
Structured elastomeric composites (SECs) with electrically conductive fillers display anisotropic piezoresistivity. The fillers do not form string-of-particle structures but pseudo-chains formed by grouping micro-sized clusters containing nanomagnetic particles surrounded by noble metals (e.g. silver, Ag). The pseudo-chains are formed when curing or preparing the composite in the presence of a uniform magnetic field, thus pseudo-chains are aligned in the direction of the field. The electrical conduction through pseudo-chains is analyzed and a constitutive model for the anisotropic reversible piezoresistivity in SECs is proposed. Several effects and characteristics, such as electron tunnelling, conduction inside the pseudo-chains, and chain-contact resistivity, are included in the model. Experimental results of electrical resistance, R, as a function of the normal stress applied in the direction of the pseudo-chains, P, are very well fitted by the model in the case of Fe3O4[Ag] microparticles magnetically aligned while curing in polydimethylsiloxane, PDMS. The cross sensitivity of different parameters (like the potential barrier and the effective distance for electron tunnelling) is evaluated. The model predicts the presence of several gaps for electron tunnelling inside the pseudo-chains. Estimates of those parameters for the mentioned experimental system under strains up to 20% are presented. Simulations of the expected response for other systems are performed showing the influence of Young's modulus and other parameters on the predicted piezoresistivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...