Creation of liquid-crystal periodic zigzags by surface treatment and thermal annealing†
Abstract
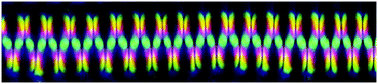
The orientation control of soft matter to create a large area single domain is one of the most exciting research topics in materials science. Recently, this effort has been extended to fabricate two- or three-dimensional structures for electro-optical applications. Here, we create periodic zigzag structures in liquid crystals (LCs) using a combination of surface treatment and thermal annealing. The LC molecules in the nematic (N) phase were initially guided by the alignment layer of rubbed polymers, which were quenched and subsequently annealed in the smectic A (SmA) phase to create periodic zigzag structures that represent modulated layer structures. Direct investigation of the zigzags was performed using microscopy and diffraction techniques, showing the alternately arranged focal conic domains (FCDs) formed. The resulting macroscopic periodic structures will be of interest in further studies of the physical properties of soft matters.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...