Effects of protonation on foaming properties of dodecyldimethylamine oxide solutions: a pH-study†
Abstract
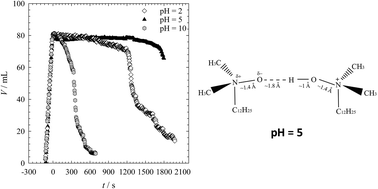
The critical micelle concentration (cmc), the surface excess (Γ), as well as the micelle aggregation number (m) of the surfactant dodecyldimethylamine oxide (C12DMAO) have been reported to strongly depend on the pH-value of the aqueous surfactant solution. At high ionic strength, the cmc displays a minimum, while both Γ and m have a maximum at a pH-value close to the pKa of the surfactant. These experimental observations have been explained as being due to specific hydrogen bonds between the head groups, which are formed once the surfactant is partly or fully protonated. This investigation addresses the question of whether the pH also affects the foaming properties of C12DMAO solutions. To answer this question we measured the foamability and the foam stability of C12DMAO solutions at a fixed C12DMAO concentration of 5 cmc for five different pH-values, namely pH = 2, 3, 5, 8, and 10. We found that the foamability is hardly affected by the pH-value, while the foam stability strongly depends on the pH. As is the case for the above mentioned properties, the foam stability also displays an extremum in the studied pH-range, namely a maximum at pH = 5. We discuss our results in terms of the hydrogen bond hypothesis and show that this hypothesis indeed is in line with the observed trend for the foam stability. Moreover, we discuss that hydrogen bond formation may rationalize how the molecular structure of a surfactant affects foam stability.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...