Silica nanoparticles as tracers of the gelation dynamics of a natural biopolymer physical gel
Abstract
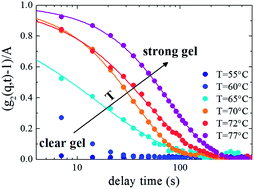
The gelation of methylcellulose in water has been studied by X-ray photon correlation spectroscopy, electrophoresis and rheological measurements by looking into the dynamics of silica nanoparticles as tracers in the polymer matrix. The temperature and scattering vector dependence of the structural relaxation time is investigated at the nanometric length scale during the formation of the strong gel state. We find a stress-dominated dynamics on approaching the gel state, characterized by a hyper-diffusive motion of the silica particles. These results support the idea of a unifying scenario for the dynamics of complex out of equilibrium soft materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...