Coulombic free energy and salt ion association per phosphate of all-atom models of DNA oligomer: dependence on oligomer size†
Abstract
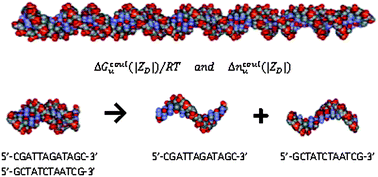
We investigate how the coulombic Gibbs free energy and salt ion association per phosphate charge of DNA oligomers vary with oligomer size (i.e. number of charged residues |ZD|) at 0.15 M univalent salt by non-linear Poisson Boltzmann (NLPB) analysis of all-atom DNA models. Calculations of these quantities (Gcoulu, ncoulu) are performed for short and long double-stranded (ds) and single-stranded (ss) DNA oligomers, ranging from 4 to 118
- This article is part of the themed collection: Polyelectrolytes in Soft Matter and Biology

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...