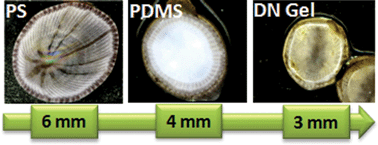
In this paper, settlement, metamorphosis, and long term growth of barnacles on soft substrates with a wide elasticity range (modulus 0.01–0.47 MPa) as well as with the variation in wettability were investigated for the first time in vitro, in the laboratory environment. Tough double-network (DN) hydrogels and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) were used as the soft hydrophilic substrates and hydrophobic substrates, respectively, and polystyrene (PS), a hard and hydrophobic substrate, was used as a control. It was observed that (1) the initial settlement and metamorphosis of cyprid larvae dramatically increase with the substrate elastic modulus while not showing an explicit dependence on the substrate wettability; (2) the growth rate of barnacles on both DN gels and PDMSs does not show an explicit dependence on the elasticity of the soft substrates, while it shows a slightly higher value on the hydrophobic PDMSs than on the hydrophilic DN gels; (3) the growth rate on these soft substrates is explicitly lower than that on the rigid PS substrate at the late stage of the growth; (4) the “self-release” phenomenon of barnacles was observed for the PDMS substrate with a modulus higher than 0.01 MPa. Based on these observations, the antifouling effects of the soft substrates on barnacles were discussed.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...