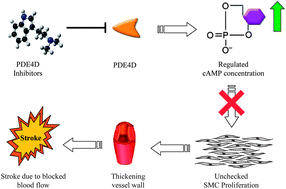
Phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) has been identified be a promising target which associate with stroke, which is one of the top 3 leading of death and main leading cause of adult disability in US. In this study, we applied virtual screening on the world's largest traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) database (http://tcm.cmu.edu.tw;1 C. Y. C. Chen, PLoS One, 2011, 6, e15939) for natural compounds that inhibit PDE4D functions. Molecular docking and dynamics simulation were employed to investigate the protein–ligand interactions of compounds with top two dock scores. During the simulation, the divalent metal cations in PDE4D formed stable hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions between ligand and binding site residues. Furthermore, the two top TCM candidates, 2-O-caffeoyl tartaric acid and mumefural, formed additional steady hydrogen bond with binding site residue and active site residue respectively. The additional hydrogen bonds further stabilize protein-ligand interaction at the PDE4D binding site. To predict the bioactivity of the top TCM candidates, we built two prediction models using multiple linear regression (MLR) and support vector machine (SVM). The predicted pIC50 values suggest that 2-O-caffeoyl tartaric acid and mumefural are potential PDE4D inhibitors.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...