Selective catalytic conversion of waste lignocellulosic biomass for renewable value-added chemicals via directional microwave-assisted liquefaction†
Abstract
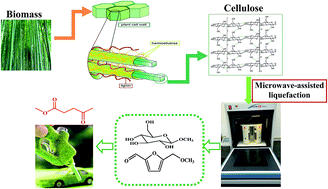
Selective catalytic conversion of biomass waste for producing methyl levulinate (MLA) via directional microwave-assisted liquefaction was investigated. The goal of the study was to develop a directional liquefaction process using dielectric heating with microwave energy. The methanolysis of biomass into methyl levulinate was studied in the presence of several acid catalysts. The C6 sugar substrates in biomass were successfully converted into methyl levulinate under the optimized conditions (180 °C, 40 min) with a yield of 29.39 wt%. 5-Hydroxymethyl furfural, glucose, fructose, cellobiose, corn starch, and microcrystalline cellulose were selected as models for directional microwave-assisted liquefaction. Therefore, the possible reaction pathway of biomass to methyl levulinate could be investigated. The selective catalytic conversion of biomass was found to be highly efficient for the generation of MLA (reaching a maximum yield of approximately 30 wt%), higher than the levulinic acid yield (14 wt%) in aqueous solution under the same reaction conditions. The results suggested that directional microwave-assisted liquefaction is an effective method that can produce a high value-added fuel additive (methyl levulinate) from lignocellulosic biomass under designated reaction processes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...