A sustainable and efficient process for the preparation of polyethylene–polystyrene interpolymer based anion exchange membranes by in situ chloromethylation for electrodialytic applications†
Abstract
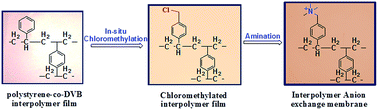
The present article describes the preparation of efficient and stable anion exchange membranes (AEMs) from the inter-polymer of polyethylene and polystyrene-co-polydivinylbenzene. The chloromethylated moiety in the interpolymer film was incorporated by an in situ Friedel–Crafts reaction followed by quaternization with trimethylamine. This process dispensed the direct use of hazardous and carcinogenic chloromethyl ether which is required for functionalization of interpolymer films. The effects of mole ratio of reactants during the electrophilic substitution reaction were investigated and the degree of chloromethylation was optimized. The anion exchange membrane was characterized by ATR-IR spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, stress–strain properties, ion-exchange capacity and water uptake. The electrochemical properties such as the membrane resistance, ionic conductivity and transport number were also determined. The oxidative stability of the membrane was verified by treatment with 3% Fenton's reagent at room temperature. The performance of the membrane in terms of water desalination by electrodialysis and ultrapure water production by the electrodeionization process was evaluated and compared with those of polyethylene–poly-4-methylstyrene interpolymer based membranes and two other commercial membranes (Ionsep and Fujifilm).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...