Catalysis with chalcogen bonds: neutral benzodiselenazole scaffolds with high-precision selenium donors of variable strength†
Abstract
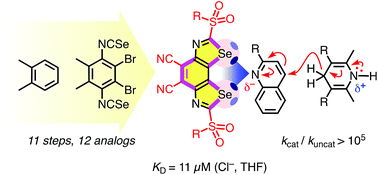
The benzodiselenazoles (BDS) introduced in this report fulfill, for the first time, all the prerequisites for non-covalent high-precision chalcogen-bonding catalysis in the focal point of conformationally immobilized σ holes on strong selenium donors in a neutral scaffold. Rational bite-angle adjustment to the long Se–C bonds was the key for BDS design. For the unprecedented BDS motif, synthesis of 12 analogs from o-xylene, crystal structure, σ hole variation strategies, optoelectronic properties, theoretical and experimental anion binding as well as catalytic activity are reported. Chloride binding increases with the depth of the σ holes down to KD = 11 μM in THF. Catalytic activities follow the same trend and culminate in rate enhancements for transfer hydrogenation of quinolines beyond 100 000.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...