Harnessing fungal nonribosomal cyclodepsipeptide synthetases for mechanistic insights and tailored engineering†
Abstract
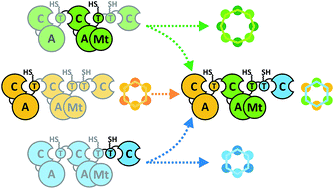
Nonribosomal peptide synthetases represent potential platforms for the design and engineering of structurally complex peptides. While previous focus has been centred mainly on bacterial systems, fungal synthetases assembling drugs like the antifungal echinocandins, the antibacterial cephalosporins or the anthelmintic cyclodepsipeptide (CDP) PF1022 await in-depth exploitation. As various mechanistic features of fungal CDP biosynthesis are only partly understood, effective engineering of NRPSs has been severely hampered. By combining protein truncation, in trans expression and combinatorial swapping, we assigned important functional segments of fungal CDP synthetases and assessed their in vivo biosynthetic capabilities. Hence, artificial assembly line components comprising of up to three different synthetases were generated. Using Aspergillus niger as a heterologous expression host, we obtained new-to-nature octa-enniatin (4 mg L−1) and octa-beauvericin (10.8 mg L−1), as well as high titers of the hybrid CDP hexa-bassianolide (1.3 g L−1) with an engineered ring size. The hybrid compounds showed up to 12-fold enhanced antiparasitic activity against Leishmania donovani and Trypanosoma cruzi compared to the reference drugs miltefosine and benznidazole, respectively. Our findings thus contribute to a rational engineering of iterative nonribosomal assembly lines.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...