The rational design of specific SOD1 inhibitors via copper coordination and their application in ROS signaling research†
Abstract
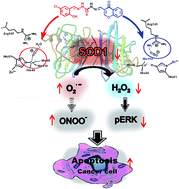
Efficient methods for the regulation of intracellular O2˙− and H2O2 levels, without altering intracellular processes, are urgently required for the rapidly growing interest in ROS signaling, as ROS signaling has been confirmed to be involved in a series of basic cellular processes including proliferation, differentiation, growth and migration. Intracellular H2O2 is formed mainly via the catalytic dismutation of O2˙− by SODs including SOD1, SOD2 and SOD3. Thus, the intracellular levels of O2˙− and H2O2 can directly be controlled through regulating SOD1 activity. Here, based on the active site structure and catalytic mechanism of SOD1, we developed a new type of efficient and specific SOD1 inhibitors which can directly change the intracellular levels of H2O2 and O2˙−. These inhibitors inactivate intracellular SOD1 via localization into the SOD1 active site, thereby coordinating to the Cu2+ in the active site of SOD1, blocking the access of O2˙− to Cu2+, and breaking the Cu2+/Cu+ catalytic cycle essential for O2˙− dismutation. The reduced ERK1/2 phosphorylation induced by the specific SOD1 inactivation-mediated decrease of intracellular H2O2 levels reveals the potential of these specific SOD1 inhibitors in understanding and regulating ROS signaling. Furthermore, these specific SOD1 inhibitors also lead to selectively elevated cancer cell apoptosis, indicating that these kinds of SOD1 inhibitors might be candidates for lead compounds for cancer treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...