Switching of the solid-state guest selectivity: solvent-dependent selective guest inclusion in a crystalline macrocyclic boronic ester†
Abstract
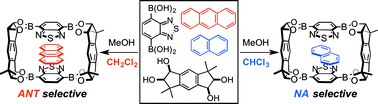
Selective inclusion of each of bicyclic and tricyclic aromatic guest molecules was realized utilizing the self-assembly of a crystalline benzothiadiazole-type macrocyclic boronic ester. The complete switching of the guest selectivity was achieved simply by changing the cosolvent used in the formation of the crystalline host–guest complexes. Both the association free energy of host–guest complexes and the stability of packing structure were found to play important roles for the determination of the guest selectivity in this system, and the critical role of solvent molecules in the crystalline state for the switching phenomena was clarified.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...