A ratiometric NMR pH sensing strategy based on a slow-proton-exchange (SPE) mechanism†
Abstract
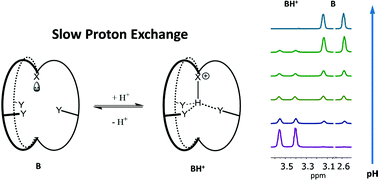
Real time and non-invasive detection of pH in live biological systems is crucial for understanding the physiological role of acid–base homeostasis and for detecting pathological conditions associated with pH imbalance. One method to achieve in vivo pH monitoring is NMR. Conventional NMR methods, however, mainly utilize molecular sensors displaying pH-dependent chemical shift changes, which are vulnerable to multiple pH-independent factors. Here, we present a novel ratiometric strategy for sensitive and accurate pH sensing based on a small synthetic molecule, SPE1, which exhibits exceptionally slow proton exchange on the NMR time scale. Each protonation state of the sensor displays distinct NMR signals and the ratio of these signals affords precise pH values. In contrast to standard NMR methods, this ratiometric mechanism is not based on a chemical shift change, and SPE1 binds protons with high selectivity, resulting in accurate measurements. SPE1 was used to measure the pH in a single oocyte as well as in bacterial cultures, demonstrating the versatility of this method and establishing the foundation for broad biological applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...