A facile route to electronically conductive polyelectrolyte brushes as platforms of molecular wires†
Abstract
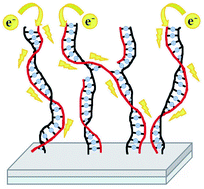
A facile strategy for the synthesis of conjugated polyelectrolyte brushes grafted from a conductive surface is presented. Such brushes form a platform of molecular wires oriented perpendicularly to the surface, enabling efficient directional transport of charge carriers. As the synthesis of conjugated polymer brushes using chain-growth polymerization via a direct “grafting from” approach is very challenging, we developed a self-templating surface-initiated method. It is based on the formation of multimonomer template chains in the first surface-initiated polymerization step, followed by the second polymerization leading to conjugated chains in an overall ladder-like architecture. This strategy exploits the extended conformation of the surface-grafted brushes, thereby enabling alignment of the pendant polymerizable groups along the template chains. We synthesized a new bifunctional monomer and used the developed approach to obtain quaternized poly(ethynylpyridine) chains on a conductive indium tin oxide surface. A catalyst-free quaternization polymerization was for the first time used here for surface grafting. The presence of charged groups makes the obtained brushes both ionically and electronically conductive. After doping with iodine, the brushes exhibited electronic conductivity, in the direction perpendicular to the surface, as high as 10−1–100 S m−1. Tunneling AFM was used for mapping the surface conductivity and measuring the conductivity in the spectroscopic mode. The proposed synthetic strategy is very versatile as a variety of monomers with pendant polymerizable groups and various polymerization techniques may be applied, leading to platforms of molecular wires with the desired characteristics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...