Humidity-dependent surface tension measurements of individual inorganic and organic submicrometre liquid particles†
Abstract
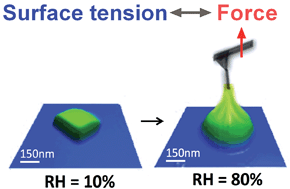
Surface tension, an important property of liquids, is easily measured for bulk samples. However, for droplets smaller than one micron in size, there are currently no reported measurements. In this study, atomic force microscopy (AFM) and force spectroscopy have been utilized to measure surface tension of individual submicron sized droplets at ambient pressure and controlled relative humidity (RH). Since the surface tension of atmospheric aerosols is a key factor in understanding aerosol climate effects, three atmospherically relevant systems (NaCl, malonic and glutaric acids) were studied. Single particle AFM measurements were successfully implemented in measuring the surface tension of deliquesced particles on the order of 200 to 500 nm in diameter. Deliquesced particles continuously uptake water at high RH, which changes the concentration and surface tension of the droplets. Therefore, surface tension as a function of RH was measured. AFM based surface tension measurements are close to predicted values based on bulk measurements and activities of these three chemical systems. Non-ideal behaviour in concentrated organic acid droplets is thought to be important and the reason for differences observed between bulk solution predictions and AFM data. Consequently, these measurements are crucial in order to improve atmospheric climate models as direct measurements hitherto have been previously inaccessible due to instrument limitations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...