Polythiazole linkers as functional rigid connectors: a new RGD cyclopeptide with enhanced integrin selectivity†
Abstract
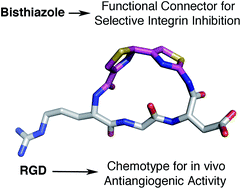
Polythiazole amino acids clasp linear peptides to generate cyclic derivatives, however, the resulting species are not merely stapled peptides but bear a complex heterocyclic moiety displaying its intrinsic set of interactions. As a proof of concept, a bisthiazole moiety has been grafted onto an RGD sequence to deliver a new cilengitide analogue with improved integrin selectivity and remarkable in vivo antiangiogenic activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...