Efficient gene delivery into cells by a surprisingly small three-armed peptide ligand†
Abstract
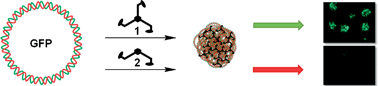
The development of new non-viral transfection vectors for gene transport into cells is of current interest. A small, three-armed peptide ligand 1 is derived from the cationic dipeptide Lys-Phe with an additional anion recognition site at its N-terminus, binds to DNA with high affinity (K ca. 107 M−1) and efficiently delivers a GFP plasmid into cells. Compared to the cationic polymer polyethyleneimine (PEI), routinely used as a standard vector for transfection, 1 is significantly more efficient and also less cytotoxic. As DLS and AFM studies show, ligand 1 condenses DNA into tightly packed cationic aggregates which are then taken up by the cells. In contrast, the analogous divalent peptide ligand 2 of identical amino acid sequence and the highly charged divalent DNA-binder 3 (Lys-Lys-Arg) do not enable gene delivery though they also bind with high affinity (2: K ca. 106 M−1; 3: K ca. 107 M−1). All three ligands are able to transfer genetic material into cells but only the trivalent gene carrier is able to escape from the endosome due to its superior buffering capacity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...