Switching of non-helical overcrowded tetrabenzoheptafulvalene derivatives†
Abstract
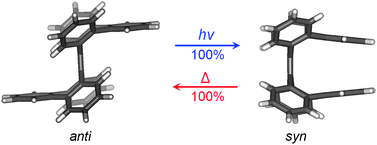
This study explores a series of non-helical overcrowded tetrabenzoheptafulvalene derivatives, which are different from the parent tetrabenzoheptafulvalene (1) by avoiding terminal C–C double bonds, detailing their synthesis, characterization and syn/antiisomerization. The most interesting findings from this study are that the syn and anti isomers of three overcrowded tetrabenzoheptafulvalene derivatives (3–5) can be switched by photo- and thermal isomerizations both in very high yields. The predominance of syn isomer in the photoisomerization has been explained with DFT calculations in terms of the arrangement of the excited- and ground-state potential energy surfaces. The less stable syn isomer of an overcrowded tetrabenzoheptafulvalene derivative thermally isomerizes to the corresponding anti isomer through seven-membered ring flipping, and the energy barrier of thermal isomerization is found to be directly related to the rigidity and crowdedness of the seven-membered rings. These findings suggest that overcrowded tetrabenzoheptafulvalene derivatives are promising building blocks for molecular switches and machines. In addition, the new synthesis and unambiguous characterization of hexabenzoheptafulvalene (4) have also led to correction of the previously claimed synthesis of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...