A combination of docking and cheminformatics approaches for the identification of inhibitors against 4′ phosphopantetheinyl transferase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis†
Abstract
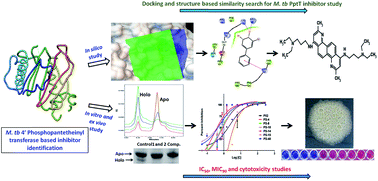
4′ Phosphopantetheinyl transferase (PptT) is involved in post translational modification by carrying out phosphopantetheinylation of proteins in non-ribosomal peptide synthesis and polyketide synthesis pathways of various organisms. PptT was recently shown to be crucial for the survival as well as persistence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tb) in mice models thus demonstrating it to be an attractive drug target. By employing Autodock 4.2 and Glide, we virtually screened the filtered NCI library against the active site of PptT and out of the 205 molecules tested in vitro, 13 molecules exhibited potent enzyme inhibition with IC50 ≤ 10 μg ml−1. Further evaluation of the molecules against the in vitro growth of M. tb resulted in the identification of six compounds that exhibited inhibition of both enzyme activity as well as M. tb growth. Subsequently, a cheminformatics based structure similarity approach led to the identification of 5 analogues of P-52 (IC50 – 2.25 μg ml−1 and MIC90 – 77.5 μg ml−1) with IC50 ≤ 1 μg ml−1 thereby establishing N,N-diethyl-N′-(2-methylquinolin-8-yl)propane-1,3-diamine as one of the potent inhibitory scaffolds of PptT. The inhibitors were further evaluated for their MIC90 values as well as cytotoxicity against various mammalian cell lines. PS-40 (NSC-328398), an analogue of P-52, emerged as a potent inhibitory molecule which exhibited an IC50 of 0.25 μg ml−1, MIC90 of 10 μg ml−1 and negligible cytotoxicity with a selectivity index >10 against three mammalian cell lines tested. Thus, our study identified potent inhibitory scaffolds against 4′ phosphopantetheinyl transferase of M. tb, an important drug target of M. tb.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...