Selective capture and rapid identification of E. coli O157:H7 by carbon nanotube multilayer biosensors and microfluidic chip-based LAMP†
Abstract
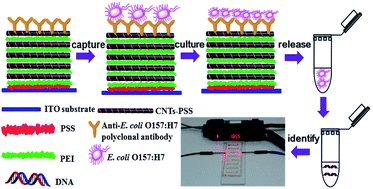
We describe a sensitive approach for visual and point-of-care detection of E. coli O157:H7 and its toxic gene by combining carbon nanotube (CNT) multilayer biosensors and microfluidic chip-based loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). The anti-E. coli O157:H7 functionalized CNT multilayer biosensor can selectively capture the target bacterium E. coli O157:H7 in complex samples. After culturing, the captured bacteria can be released on demand by cleavage of the anti-E. coli O157:H7 antibody–bacteria interaction. The DNA concentration of the released bacteria was subsequently analyzed with microfluidic chip-based LAMP. After systematic optimization of capturing and detecting conditions, the proposed sensing platform was capable of detecting concentrations as low as 1 CFU mL−1 without complicated instrumentation, this is much more sensitive than previous reported methods. The distinct advantages of the proposed sensing platform, such as high specificity, low cost, good reproducibility and the ability of regenerating, make it a potential platform for detecting E. coli O157:H7 in related food safety and clinical diagnosis.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating Excellence in Research: 100 Women of Chemistry


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...