Immobilization of tyrosinase on polyacrylonitrile beads: biodegradation of phenol from aqueous solution and the relevant cytotoxicity assessment
Abstract
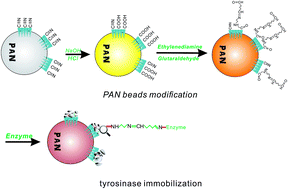
An economical and stabilized immobilized-enzyme method was developed for the removal of phenol in wastewater. Tyrosinase was immobilized on the PAN-based beads with glutaraldehyde as was confirmed successfully by a series of characterizations involving Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). The biodegradation of phenol was investigated by using the immobilized beads and compared to free tyrosinase. The optimum pH and temperature were determined to be 7.0 and 40 °C, respectively. Experiments showed that the immobilized tyrosinase was much more stable than the free tyrosinase in storage and that the immobilized tyrosinase could even retain about 78% of its original activity after repeated use 6 times in a batch system. Furthermore, the comparative in vitro cytotoxicity of phenol/treated solutions were evaluated in LO2 and HepG2 cells by using the CCK-8 assay for cell viability along with flow cytometry detection for apoptosis. The results showed that the toxicity of the phenol solutions only exerted toxicity on cells in a certain concentration range (>0.5 mM for LO2 and HepG2 cells) and that the toxicity of the phenol solutions was greatly decreased after treatment with the tyrosinase-immobilized beads. Thereby, the results confirm that we have established a suitable strategy with promising application to remove phenol economically and efficiently, which could even lower the toxicity of phenol at the cellular level.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...