Bicrystalline TiO2 heterojunction for enhanced organic photodegradation: engineering and exploring surface chemistry†
Abstract
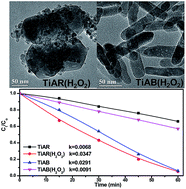
Bicrystalline TiO2 anatase/rutile (TiAR) and anatase/brookite (TiAB) have been extensively studied for photocatalysis, but the differences in their surface chemistry (defect and non-defect) are still not well understood. Here we integrated treatment effect and phase heterojunction effect to engineer the surface chemistry of TiAR and TiAB. TiAR and TiAB were either reduced by H2 or oxidized by H2O2. TiAR consisted of nanoparticle (anatase) patched nanobricks (rutile), while TiAB was predominated with nanorods. After treatment, both of them retained their morphologies, crystal structure, and porosities. We found that untreated TiAB demonstrated a twice higher activity than TiAR in methylene orange (MO) degradation, mainly because of the more facilitated charge transfer between the anatase and brookite interface, exposure of surface Ti3+/O2− radicals, and the positively charged surface in TiAB. Interestingly, H2-reduced TiAR and TiAB showed a decrease in activity compared to their counterparts, while H2O2-treated TiO2 went through different mechanisms. H2O2 treatment induced a gradual decrease in the activity of TiAB(H2O2), depending on the treatment temperature. By contrast, TiAR(H2O2) showed three times enhancement in activity that was comparable to the most active TiAB. The findings in this work provided new insights that rather than crystallinity, particle size, surface area, and band gap, the photocatalytic performance of TiO2 is closely associated with the phase junction, surface charge and defect sites (Ti3+/vacancy).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...