Fabrication of sponge-like α-Ni(OH)2 on styrene–acrylonitrile copolymer (SAN)-derived carbon spheres as electrode materials for supercapacitor application
Abstract
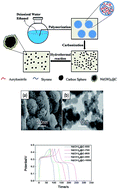
Styrene–acrylonitrile copolymer particles (SANPs) were synthesized through dispersion polymerization. Their high residual carbon content and abundant nitrogen is beneficial for electrochemical performance. In this work, the SANPs were used as the carbon precursor to prepare a series of different carbon spheres by carbonization at various temperatures. Then, α-Ni(OH)2 was coated on the above carbon backbones via the hydrothermal method to give sponge-like morphologies. The nanostructures of both the SANPs and the nanocomposites were fully investigated by scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction spectroscopy, and Raman analysis. The electrochemical studies found that when the carbonization temperature of the SANPs was 900 °C, the composite could achieve a high specific capacitance of 333.84 F g−1 at a current density of 0.5 A g−1, with 75.34% capacitance retention of the initial value after 3000 cycles. The capacitances of the composites are greatly influenced by the carbonization conditions of the SANPs and the special core–shell structures with their sponge-like surface morphologies.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...