Cauliflower-like Ni/NiO and NiO architectures transformed from nickel alkoxide and their excellent removal of Congo red and Cr(vi) ions from water†
Abstract
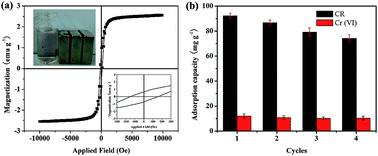
Cauliflower-like nickel alkoxide, Ni/NiO and NiO architectures were synthesized via a reflux route using NaBH4–EG as alkaline precipitant. The as-prepared powders were characterized by XRD, FESEM, TEM, HRTEM, and N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms. The results show that the nickel alkoxide is made up of smooth spherical building blocks with diameters of about 500 nm that aggregate interactively to form whole 3D structures. The Ni/NiO and NiO architectures can be obtained by the direct thermal transformation from nickel alkoxide precursor at 300 °C and 600 °C, respectively, which are assembled by nanoparticles and composed of mesopores and macropore. The as-prepared three samples exhibit excellent performance for the removal of Congo red (CR) and Cr(VI) pollutant from aqueous solutions due to their hierarchical structures and high specific surface areas. The corresponding adsorption process fits well with the pseudo-second-order kinetics model and the Langmuir model. Compared with nickel alkoxide and NiO, Ni/NiO architectures show the highest adsorption performance, with the maximum capacity of 642.37 and 92.52 mg g−1 for CR and Cr(VI), respectively. Further, the easily magnetic separation and reused clearly suggests that the Ni/NiO architectures can be explored as an excellent adsorbent for the removal of organic dye and heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...