Palladium(0) nanoparticles supported on polydopamine coated Fe3O4 as magnetically isolable, highly active and reusable catalysts for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane†
Abstract
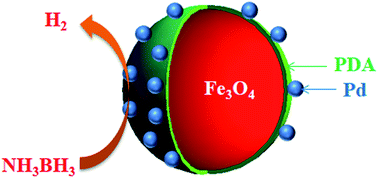
Magnetic ferrite nanopowders were coated with polydopamine which is inert against the hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Coating of ferrite powders was achieved by pH-induced self-polymerization of dopamine hydrochloride at room temperature. Palladium(0) nanoparticles supported on polydopamine coated ferrite (Pd0/PDA–Fe3O4) were prepared by impregnation of palladium(II) ions on the surface of PDA–Fe3O4 followed by their reduction with sodium borohydride in aqueous solution at room temperature. Magnetically isolable Pd0/PDA–Fe3O4 catalysts were characterized by a combination of advanced analytical techniques. The results reveal that palladium nanoparticles with an average size of 2.0 ± 0.4 nm are well dispersed on polydopamine layer with a thickness of 3.0 ± 0.5 nm on the surface of ferrite nanopowders. Pd0/PDA–Fe3O4 with a palladium loading of 3.81% wt was found to be a highly active and reusable catalyst in hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of ammonia borane with a turnover frequency value of 14.5 min−1 at 25.0 ± 0.1 °C. Magnetically isolable Pd0/PDA–Fe3O4 catalysts preserve their initial catalytic activity even after the tenth use providing the release of 3 equivalent H2 per mole of ammonia borane. The report also includes the results of kinetic studies on the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane performed at various temperatures and different catalyst concentrations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...