Synthesis of well-defined core–shell nanoparticles based on bifunctional poly(2-oxazoline) macromonomer surfactants and a microemulsion polymerization process†
Abstract
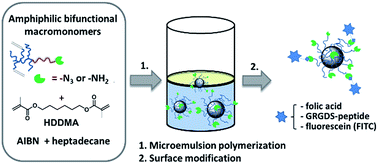
Particles in the sub-100 nm range have attracted widespread attention in the past few years due to their application in drug delivery and diagnostics. Here we describe the synthesis of two bifunctional, amphiphilic poly(2-oxazoline) macromonomers with multiple acrylate groups in their hydrophobic block and azide or primary amino end groups. The amphiphilic macromonomers were applied in a microemulsion polymerization to form well-defined core-crosslinked nanoparticles with surface functional azide or amine groups. Therefore, an amphiphilic poly(2-oxazoline) was prepared by cationic ring-opening polymerization of 2-methyl-2-oxazoline to form the hydrophilic block and a mixture of 2-heptyl-2-oxazoline and 2-(5-pentyl-[(1,2,3-triazol)-4-yl-methacrylat)]-oxazoline to form the hydrophobic block and was terminated with an azide moiety as end group. The introduction of multiple methacrylate groups into the poly(2-oxazoline) macromonomers serve as a stabilizer in the microemulsion process to covalently link the polymer to the particle core. Variable particle sizes of 20–75 nm have been prepared by encapsulating different amounts of 1,6-hexanedioldimethacrylate (HDDMA) to swell the micellar core before subsequent crosslinking takes place. Finally, particle surface functionalization was achieved by converting the terminal azide group via Staudinger-reaction to a primary amine group. Nanoparticles with surface primary amine groups were functionalized with folic acid (FA), a GRGDS-peptide derivative and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) by simple amidation reaction (FA, RGD-peptide) or thiourea formation (FITC).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...