Enhanced conversion and stability of biosynthetic selenium nanoparticles using fetal bovine serum†
Abstract
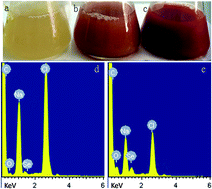
Compared with chemical methods, biosynthesis provides a mild and green synthesis pathway for selenium nanoparticles, and biosynthetic selenium nanoparticles (BioSeNPs) exhibit more uniformity with high electron density. However, there are still many challenges in the synthesis and storage of BioSeNPs. This study aimed to optimize BioSeNPs synthesis using fetal bovine serum (FBS) as part of the culture medium to enhance the conversion efficiency and stability of BioSeNPs. LB medium without FBS addition was also used to synthesize BioSeNPs as a control. Red selenium nanoparticles in the hexagonal phase were synthesized through the reduction of selenite by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. High conversion efficiency, up to 98.5%, was obtained with 20% FBS addition, while the conversion efficiency was only 73.6% in LB medium. This might be attributed to the variety of proteins and growth factors in FBS. FTIR and XPS analyses showed that many functional groups, such as hydroxyl, amide and carbonyl, were detected on the surface of the BioSeNPs, and more C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bonds and proteins were found in FBS-BioSeNPs, resulting in strong electrostatic repulsion between the nanoparticles, which is against aggregation. These results were in agreement with zeta potential analysis that FBS could improve the stability of BioSeNPs.
O bonds and proteins were found in FBS-BioSeNPs, resulting in strong electrostatic repulsion between the nanoparticles, which is against aggregation. These results were in agreement with zeta potential analysis that FBS could improve the stability of BioSeNPs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...