Gas-phase kinetic and mechanistic investigation of the OH radical and Cl atom oxidation of tetraethoxysilane
Abstract
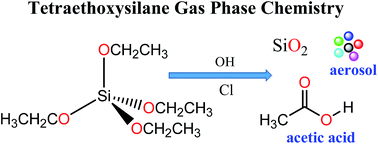
Rate coefficients have been determined in a large photoreactor for the reaction of OH radicals and Cl atoms with tetraethoxysilane (TEOS, (CH3CH2O)4Si) using a relative kinetic method and in situ FTIR spectroscopy for the analysis. Values of (2.99 ± 0.37) × 10−11 and (2.41 ± 0.47) × 10−10 cm3 per molecule per s were obtained for the reactions of OH and Cl with TEOS, respectively, at 298 K and atmospheric pressure. The products originating from the OH-radical and Cl-atom initiated oxidation of TEOS have also been investigated. Acetic acid (CH3C(O)OH) is observed as a major product in both cases with a molar yield of (95 ± 4)%. An oxidation mechanism is proposed to explain its formation and the possible identity of the co-product(s) is discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...