Template-induced in situ dispersion of enhanced basic-sites on sponge-like mesoporous silica and its improved catalytic property†
Abstract
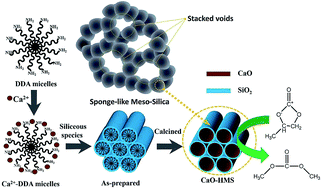
Catalytic performance of heterogeneous catalysis is strongly dependent on the dispersity of catalytic active sites, and especially a high exposure of the unit active phase is promising for the overall catalytic process. In this study, a novel strategy was developed to fabricate an unprecedented CaO-based mesoporous solid strong base catalyst. Relying on the physicochemical assembly of Ca2+ in the interface between a micelle and siliceous wall, thin-layer-like calcium oxide species were formed in situ and dispersed in the mesochannels of silica. Wherein, the gradual coverage of CaO on the mesoporous wall was controlled by adjusting the amounts of Ca2+ on alkylamine micelles. Interestingly, a novel sponge-like microscale structure of silica was discovered in the CaO-based mesoporous-composites for the first time, which completely differs from the reported mesoporous silica. More importantly, the introducing of a CaO solid base on the pore wall is nearly non-destructive for the textural properties of the mesoporous matrix. The direct template-induced mesoporous solid strong base not only received extremely dispersed and unexpected enhanced strong basic sites (CO2-desorption temperature ≥718 °C), but also avoided repeated thermal processes for the degradation of the basic resource, and saved energy and time. This heterogeneous alkaline catalyst shows excellent catalytic activity for the synthesis of dimethyl carbonate under a milder reaction condition (30 °C, 25 min) and holds stability and reusability beyond comparison with the conventional catalysts. The dispersed and enhanced strong basic sites, combined with excellent mesoporous properties, are demonstrated to be responsible for such a high catalytic performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...