N-Acylamino-pyridine-2,6-dione based heterocyclic dyes and their oxidative ring-degradation under alkaline conditions†
Abstract
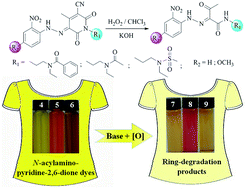
Three new N-acylamino-pyridine-2,6-dione compounds have been synthesized, which are used for the first time as coupling components to prepare corresponding heterocyclic dyes. These dyes exhibit the same hydrazone-tautomeric form both in the solid state and in solution, which have been verified by X-ray single-crystal structures and 1H NMR spectra, respectively. The reversible acid–base discoloration of the dyes has been studied via pH titration experiments, which is ascribed to the interconversion between the hydrazone and deprotonated azo forms, as evidenced by the isoabsorptive point in their UV-Vis spectra. Comparisons of their dyeing performance have been made with five commercially available pyridine-2,6-dione based disperse yellow dyes. In terms of the current problems of alkaline and oxygen instability for pyridine-2,6-dione based disperse dyes in the dyeing process, the oxidation of these dyes under alkaline conditions is further explored and three ring-degradation (ring-opening and subsequent oxidative cleavage) products are yielded. Our results clearly demonstrate that the relatively poor basic stability of pyridine-2,6-dione based dyes under oxidative conditions originates from the ring-opening of the amide unit and subsequent oxidative cleavage of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C double bond in the pyridine-2,6-dione ring.
C double bond in the pyridine-2,6-dione ring.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...