Design of a novel wound dressing consisting of alginate hydrogel and simvastatin-incorporated mesoporous hydroxyapatite microspheres for cutaneous wound healing
Abstract
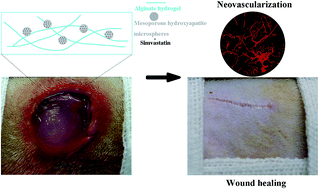
Wound dressings with pro-angiogenic activity are desirable for the rapid healing of full-thickness cutaneous wounds. It is well accepted that simvastatin can stimulate angiogenesis in addition to its lipid-lowering efficacy. However, the construction of a hydrogel-based wound dressing containing simvastatin remains a challenge due to its water-insolubility. In the present study, a novel wound dressing composed of alginate hydrogel (AH) and simvastatin-incorporated mesoporous hydroxyapatite microspheres (S-MHMs) was constructed for the sustained drug release of simvastatin. We first investigated the effect of simvastatin on the angiogenic differentiation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). The in vitro results revealed that simvastatin significantly promoted the migration and tube formation of HUVECs. Furthermore, the activation of the Akt and Erk signaling pathways was detected in HUVECs upon treatment with simvastatin, and enhanced tube formation was reversed by LY294002 and PD98059, which indicated that both the Akt and Erk signaling pathways were involved in the process of angiogenesis induced by simvastatin. Moreover, simvastatin significantly up-regulated the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which play essential roles in angiogenesis. For the in vivo experiments, simvastatin was incorporated into mesoporous hydroxyapatite microspheres (MHMs) synthesized using fructose 1,6-bisphosphate trisodium salt (FBP) as the phosphorous source by the microwave-assisted hydrothermal method. An simvastatin-loaded MHMs (S-MHMs) incorporated alginate hydrogel (S-MHMs/AH) was prepared as a wound dressing to promote the full-thickness cutaneous wound healing. The results demonstrated that S-MHMs/AH significantly enhanced new blood vessel formation and accelerated the reepithelialization of the cutaneous wounds. The present study suggests the potential application of the S-MHMs/AH composite as a novel dressing for wound healing.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...