Luminescence properties of a Zn(ii) supramolecular framework: easily tunable optical properties by variation of the alkyl substitution of (E)-N-(pyridine-2-ylethylidyne)arylamine ligands†
Abstract
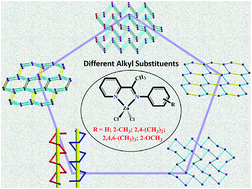
A series of different alkyl substituted of Zn(II) complexes, [ZnL1Cl2] (Zn1), [ZnL2Cl2] (Zn2), [ZnL3Cl2] (Zn3), [ZnL4Cl2] (Zn4), [ZnL5Cl2] (Zn5) ((E)-N-(pyridine-2-yl)(CMe![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NPhR), where R = H, L1; 2-CH3, L2; 2,6-(CH3)2, L3; 2,4,6-(CH3)3, L4; 2-OCH3, L5) have been synthesized and characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction, 1H NMR, FT-IR, and EA. The X-ray diffraction analyses revealed that although are all constructed by C–H⋯Cl/π hydrogen bonds and π⋯π interactions, the dimensions of these supramolecular frameworks complexes Zn1–Zn5 are quite different. Complexes Zn1 and Zn5 feature 3D 5-connected {46·64} and {44·66} topology structures, respectively, while complexes Zn2 and Zn3 feature 2D supramolecular layer with {63} topology structures. Complex Zn4 exhibits two different one-dimensional helix-shaped chains. Obviously, these results show that steric hindrance has a great impact on the final structures of the supramolecular architectures. Based on these varied structures caused by different alkyl substitutions, the emission maximum wavelengths of complexes Zn1–Zn5 can be tuned in a large range of 400–514 nm. The λem shift in the red direction after the substitution of alkyl is attributed to the HOMO–LUMO energy gap of complexes being effectively decreased due to the electron-donating ability of alkyl. These results are confirmed by the density functional theory calculations.
NPhR), where R = H, L1; 2-CH3, L2; 2,6-(CH3)2, L3; 2,4,6-(CH3)3, L4; 2-OCH3, L5) have been synthesized and characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction, 1H NMR, FT-IR, and EA. The X-ray diffraction analyses revealed that although are all constructed by C–H⋯Cl/π hydrogen bonds and π⋯π interactions, the dimensions of these supramolecular frameworks complexes Zn1–Zn5 are quite different. Complexes Zn1 and Zn5 feature 3D 5-connected {46·64} and {44·66} topology structures, respectively, while complexes Zn2 and Zn3 feature 2D supramolecular layer with {63} topology structures. Complex Zn4 exhibits two different one-dimensional helix-shaped chains. Obviously, these results show that steric hindrance has a great impact on the final structures of the supramolecular architectures. Based on these varied structures caused by different alkyl substitutions, the emission maximum wavelengths of complexes Zn1–Zn5 can be tuned in a large range of 400–514 nm. The λem shift in the red direction after the substitution of alkyl is attributed to the HOMO–LUMO energy gap of complexes being effectively decreased due to the electron-donating ability of alkyl. These results are confirmed by the density functional theory calculations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...