Highly sensitive pH dependent acetone sensor based on ultrananocrystalline diamond materials at room temperature
Abstract
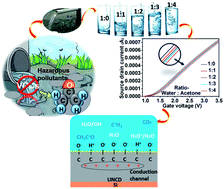
Diamond-based materials often considered inappropriate for sensor device applications, however these robust materials exhibit unpredictable electrochemical sensing properties. Herein, we report a high-performance novel acetone sensor based on diamond materials such as nanocrystalline diamond (NCD) films and ultrananocrystalline diamond (UNCD) films. A new approach has been undertaken for the selective detection of liquid acetone in water using an extended gate field effect transistor (EGFET), since these two liquids are miscible with a pH value of 7. Systematic studies revealed that ultra-high acetone sensing properties were observed from the UNCD based sensor. A higher proportion of grain boundaries exists in the UNCD film with the presence of graphitic phase (sp2 content) built conduction paths for electron transportation, as revealed by tunneling electron microscopy (TEM). The excellent sensing behavior of these UNCD based sensors was achieved owing to the reduction of the diamond-to-Si interfacial resistance, which increased the conductivity as analyzed by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) investigations. Thus the electrical conductivity of UNCD material shows an enhanced stability and reproducibility towards acetone.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...