Molybdenum disulfide nanosheet embedded three-dimensional vertically aligned carbon nanotube arrays for extremely-excellent cycling stability lithium-ion anodes†
Abstract
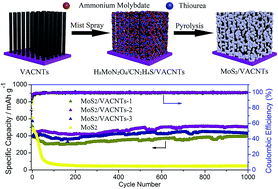
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheets embedded in three-dimensional (3D) vertically aligned carbon nanotube arrays (VACNTs) have been fabricated via a simple nebulization-assisted hydrothermal method. The MoS2/VACNTs possess a highly ordered and uniformly oriented 3D structure with MoS2 nanosheets adhering strictly to the surface of VACNTs. When evaluated as lithium-ion anode materials, so-obtained MoS2/VACNTs composites containing 52 wt% MoS2 exhibit superb electrochemical performances, including high capacity (1078 mA h g−1 at 100 mA g−1 after 1st cycle), good rate capability (789 mA h g−1 at 2000 mA g−1 after 20 cycles), and extremely-excellent cycling stability, for the MoS2/VACNTs electrode can still deliver a discharge capacity of 512 mA h g−1 after 1000 cycles at 5000 mA g−1, compared with pristine MoS2 (negligible discharge capacity at the 70th cycle). Such high electrical properties can mainly be attributed to the unique well-directed pore-morphology which provides low-resistant shortest diffusion pathways upon the high-conductive VACNTs to accelerate ion/electron movement. Moreover, the elastic spare-space inside/outside VACNTs as a buffer factor effectively restrains large volumetric change from MoS2 during the charge/discharge process. It can be determined that such a structure is attractive to achieve extremely-excellent cycling stability lithium-ion anodes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...