Non-destructive means of probing a composite polyamide membrane for characteristic free volume, void, and chemical composition
Abstract
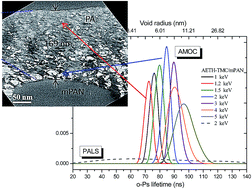
Positron annihilation spectroscopy measures free volume in membranes at the sub-nanometer scale (0.1–1 nm). In this study, we used positron annihilation age–momentum correlation (AMOC) spectroscopy coupled to a variable mono-energy slow positron beam; our objectives were to measure not only free volume but also voids that are bigger than 1 nm and to estimate the chemical composition of a composite polyamide membrane. To crosscheck these data, we also used conventional techniques: scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and quantum chemical calculations (QCC). AMOC showed that the free volume diameters and intensities in a polyamide layer were in the range of 0.42–0.68 nm and 9–3%, respectively, and that the void diameters and intensities were 7.2–14.1 nm and 12–18%, respectively, with the size distribution of the voids ranging from 5 to 20 nm. These results were consistent with those from TEM, indicating that the polyamide layer structure consisted of discrete voids distributed throughout a continuously dense phase. QCC validated the S parameter data taken from AMOC, which showed that a highly electronegative environment in the polyamide layer could inhibit the formation of positronium.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...