Potential antitumoral 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2-(1H)-ones: synthesis, in vitro biological evaluation and QSAR studies
Abstract
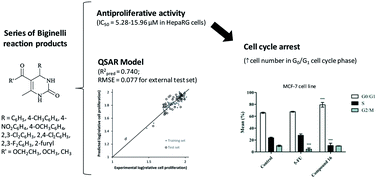
The search for novel anticancer agents with higher selectivity and lower toxicity remains a priority. This work aimed to design more potent and selective anticancer molecules among the class of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2-(1H)-ones. Thus, a series of molecules was synthesized through the Biginelli reaction and their in vitro antiproliferative activity was evaluated in different human cell lines. Then, a quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) analysis was performed using Bayesian regularized artificial neural networks to model the relationships between in silico molecular descriptors and the observed antiproliferative activity of molecules across the tested cell lines. Interestingly, among the compounds prepared, the molecules containing chloro atoms in their structure demonstrated a relevant potency and a selective antiproliferative activity against a novel hepatic cancer cell line (HepaRG) without exhibiting noticeable cytotoxicity in normal dermal cells (NHDF). However, in prostatic (LNCaP), colon (Caco-2) and breast (T47D and MCF-7) cancer cell lines generally the compounds did not exhibit relevant cytoxicity. A statistically valid QSAR model was obtained (internal validation Q2 = 0.663, RMSECV = 0.071, 10-fold cross-validation procedure, and external validation Rpred2 = 0.740, RMSE = 0.077), which allowed the analysis of the involved relationships between molecular descriptors and the reliable prediction of the antiproliferative activity for hypothetical related compounds in the studied cell lines. Moreover, flow cytometry analysis showed that in HepaRG and MCF-7 cell lines, compound 16 did not decrease cell viability but, interestingly, led to an accumulation of cells in the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle. Therefore, chlorinated 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2-(1H)-ones may be considered promising compounds for further optimization as new antitumor agents.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...