Understanding NO emissions in diesel and biodiesel based engines
Abstract
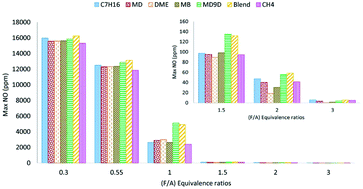
Formation of nitrogen oxide pollutants is investigated using a homogeneous combustion model for diesel and biodiesel surrogates including-n-heptane, methyl decanoate, methyl-9-decenoate and other oxygenated fuels. The investigations are carried out in a series of detailed simulation studies-ignition and combustion characteristics unique to the fuel are chosen such that comparable engine performance is obtained, and the results compared in terms of emissions. This is followed by an analysis of the NOX formation pathways for the various fuels in a model HCCI engine, operated at conditions where similar temperature profiles are obtained. Different fuel-oxygen ratios including fuel-lean, stoichiometric, and fuel-rich inlet conditions are examined in detail from viewpoint of NOX emissions. Significant NO variations are observed among the fuels at stoichiometric fuel-air ratio, with the oxygenated fuels demonstrating high NO compared to n-heptane. In particular, the NO emissions for MD9D was found to be 2.6 times that for n-heptane, at stoichiometric conditions at practically significant operating conditions. Thermal, prompt, and other pathways for NO formation are evaluated at fuel-lean, stoichiometric, and fuel-rich conditions, for different imposed temperature trends. The thermal pathway is found to contribute >60% of the NO in case of stoichiometric & fuel-lean mixtures. The contribution of the prompt pathway, on the other hand, can be as high as 50% in case of fuel-rich mixtures. Significant insight into the formation of NO in diesel and biodiesel engines is obtained from our studies.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...