Hydroxyapatite doped CeO2 nanoparticles: impact on biocompatibility and dye adsorption properties†
Abstract
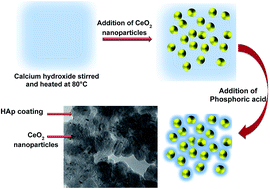
The toxicity imparted by the commercialized use of nanoparticles in environmental remediation has become a big concern. To overcome this, the current work describes the fabrication of cerium oxide (CeO2) containing hydroxyapatite (HAp) nanoparticles. The toxicity of the system was tested against the Allium cepa anaphase–telophase chromosome aberration assay. The enhanced stability and biocompatible nature of HAp widen the scope of engineered nanoproducts for wastewater treatment. Anionic Eriochrome Black T (EBT) dye was chosen as a model system for analyzing the adsorptive behavior of the engineered nanoparticles. The meticulous analysis of surface morphology, elemental composition, size and functional groups over the engineered product were ascertained by using microscopic and spectroscopic techniques. The corresponding influence of methodological aspects such as experimental pH, time, and concentration of the toxins and the nanoadsorbate toward the removal efficiency of pollutant were also quantified by using UV-Vis spectroscopic measurements. The kinetic and equilibrium adsorption analysis were also performed and a probable adsorption mechanism was determined for the prepared materials. The prepared HAp/CeO2 nanohybrid can be exploited as a competent, low-cost adsorbent for the removal of dye molecules from the aqueous environment. This piece of work validates and promotes the idea of using biocompatible and non-toxic nanomaterials for environmental remediation, with high efficiency.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...