Electrospun gelatin nanofibers loaded with vitamins A and E as antibacterial wound dressing materials†
Abstract
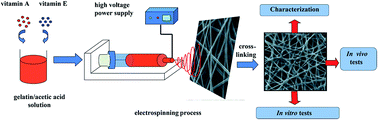
Vitamin A palmitate and vitamin E TPGS, common derivatives of the unstable vitamins A and E, were successfully incorporated into biodegradable gelatin nanofibers via electrospinning. Electron microscopy showed that smooth cylindrical fibers were produced, albeit with a small amount of beading visible for the vitamin-loaded systems. The diameters of the fibers decrease with the addition of vitamins. The presence of the vitamins in the fibers was confirmed by IR spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction showed them to exist in the amorphous physical form post-electrospinning. The addition of vitamins did not affect the hydrophilic properties of the gelatin nanofibers. Fibers containing vitamin A or E alone showed a sustained release profile over more than 60 hours, and those incorporating both vitamins showed similar release characteristics, except that the extent of release for vitamin A was increased. Antibacterial tests demonstrated that materials loaded with vitamin E were effective in inhibiting the growth of E. coli and S. aureus. The fibers could promote the proliferation of fibroblasts during the early stages of culture, and enhance the expression of collagen-specific genes. In vivo tests determined that the fibers loaded with vitamins have better wound healing performance than a commercially used antiseptic gauze and casting films.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Drug delivery and Biomaterials

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...