Structure–activity relationships of radioiodinated diphenyl derivatives with different conjugated double bonds as ligands for α-synuclein aggregates†
Abstract
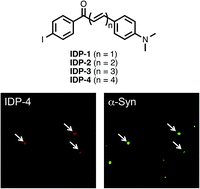
It is generally recognized that aggregates of α-synuclein (α-syn) in the brain are closely associated with the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD). Therefore, the development of in vivo imaging probes targeting α-syn aggregates is currently expected. In this study, we investigated the structure–activity relationships of radioiodinated diphenyl (IDP) derivatives with different conjugated double bonds as ligands for α-syn aggregates. An in vitro binding assay revealed that the binding affinity of the derivatives to α-syn aggregates increased as the length of the conjugated double bonds in their molecule extended. In contrast, brain uptake of the derivatives in biodistribution studies decreased in accordance with the extension of the double bonds. These findings from structure-relationship studies suggested that the length of the conjugated double bonds in the IDP derivatives plays an important role in the binding affinity for α-syn aggregates and uptake in the brain. Also, the present study may provide valuable information on molecular design for the development of new imaging probes targeting α-syn aggregates in the future.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...