High-throughput metabolic profiling for discovering metabolic biomarkers of sepsis-induced acute lung injury†
Abstract
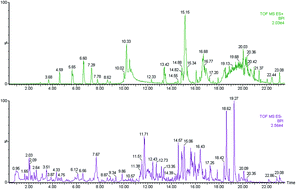
Sepsis-induced acute lung injury (ALI) remains a leading cause of death in intensive care units (ICU). Early detection is very important for improving ALI outcome. With the progress of the omics technologies, metabolomics is currently being used for biomarker discovery and identification. To accurately identify effective biomarkers of ALI, we analyzed a discovery cohort of patients in the Chinese Han population using UPLC/Q-TOF MS/MS and multivariate statistical analysis. Urine samples were collected from ALI patients in the ICU. Orthogonal partial least-squares discriminant analyses were performed for the discrimination of ALI and healthy cases. Variable importance for projection values was conducted to identify potential biomarkers. Receiver operating characteristic analysis was applied to evaluate the diagnostic power of metabolites. Supervised multivariate analysis afforded a good predictive model to distinguish their metabolic patterns. Five metabolites were identified as potential biomarkers for ALI patients. These candidate metabolites were validated in an additional independent cohort. The values of AUC range from 0.827 to 0.961 indicating the potential capacity of these metabolites for distinguishing ALI patients and healthy cases. According to the receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, 5-hydroxytryptophol glucuronide was the most potentially specific biomarker for discriminating ALI from healthy controls. This work showed that UPLC/MS metabolite phenotype profiling might be a useful tool for the effective diagnosis and further understanding of ALI.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...