Effects of pH on the alginate dialdehyde (ADA)-crosslinking of natural biological tissues and in vitro study of the endothelial cell compatibility of ADA-crosslinked biological tissues
Abstract
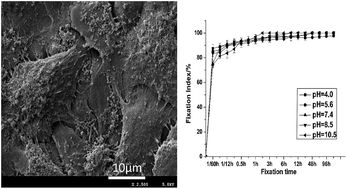
To develop new a naturally occurring crosslinking agent for overcoming the cytotoxicity of the chemical reagents used to fix bioprostheses, alginate dialdehyde, a naturally occurring crosslinking agent, was used to crosslink natural biological tissues. The effects of pH on the ADA-crosslinking of natural biological tissues and the endothelial cell compatibility of ADA-crosslinked biological tissues were investigated in this study for the first time. We crosslinked natural biological tissues (fresh porcine aortas) with ADA at different pH values (4.0, 5.6, 7.4, 8.5 and 10.5), and then determined their physicochemical properties, biomechanical properties and fibroblast-cytocompatibility. The results indicated that the biological tissue fixing by ADA at pH 7.4 showed favorable characteristics and the best cytocompatibility. Thus, the natural biological tissue fixing by ADA at pH 7.4 was used for research on the HUVEC cytocompatibility. The results obtained from the MTT assay, examination of fluorescent staining and hematoxylin & eosin (H&E) staining, and SEM-images suggested that the ADA-fixed biological tissues (at pH 7.4) possessed excellent HUVEC cytocompatibility and potential to promote endothelialization, and could be a promising material for constructing scaffolds of tissue-engineered blood vessels.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...