Effect of carbon dioxide on pore structure characteristics of dewatered lignite and the relevance to its moisture-adsorbing capacity
Abstract
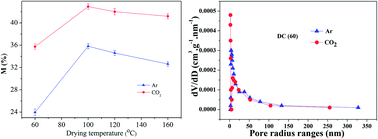
Lignite with a high moisture content is needed to effectively remove water and maximally restrain the re-adsorption capacity of dewatered coal. The ambient gas during lignite drying is an important factor influencing the physical properties of dewatered samples. CO2 is the main component of exhaust gas, which has been reused in flash drying technology. The relationship between the drying characteristics of a typical Chinese lignite and the pore structure changes of dewatered coal in a CO2 atmosphere, and the effect on the behavior of re-adsorbing moisture were studied. Drying experiments of lignite samples under an Ar atmosphere were also carried out for comparison. The moisture re-adsorption experiments of dewatered coal samples were conducted at 30 °C under relative humidity of 75%. The results show that the drying efficiency of coal samples under a CO2 atmosphere is higher than that under an Ar atmosphere due to the swelling effect caused by the adsorption of CO2, but this difference between CO2 and Ar becomes gradually smaller with increase in the drying temperature. The dewatered coal sample obtained under a CO2 atmosphere shows a stronger ability to re-adsorb moisture caused by the swelling effect, which could be attributed to the changes of the structure of the coal sample in this atmosphere and the increase of the surface area where the moisture is primarily absorbed. The total moisture content in the coal sample after re-adsorbing moisture follows a linear relationship with the specific surface area of dewatered lignite.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...