Selective oxidation of 1,2-propanediol to lactic acid catalyzed by hydroxyapatite-supported Pd and Pd–Ag nanoparticles†
Abstract
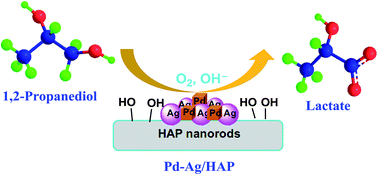
Selective catalytic oxidation of 1,2-propanediol is an alternative, effective, and environmentally benign method for producing lactic acid. Hydroxyapatite-supported Pd (Pd/HAP) and Pd–Ag (Pd–Ag/HAP) catalysts were prepared by the sol-immobilization method. The as-prepared catalysts were characterized by XRD, TEM, HRTEM, XPS, BET, and CO2-TPD techniques. The average particle sizes of Pd nanocubes in Pd/HAP catalysts were tuned from 6 to 18 nm by changing the amount of KBr and PVP, which significantly affected the 1,2-propanediol conversion and the lactic acid selectivity. Pd/HAP catalyst with cubic Pd nanoparticles was more selective to lactic acid than Pd/HAP catalyst with spherical Pd nanoparticles in the oxidation of 1,2-propanediol. The coalesced Pd and Ag nanoparticles in Pd–Ag/HAP bimetallic catalysts synergistically catalyzed the oxidation of 1,2-propanediol to lactic acid. The support HAP with high basicity promoted the oxidation of 1,2-propanediol to lactic acid. When the catalytic oxidation of 1,2-propanediol with O2 was carried out at 100 °C for 2 h in an alkaline solution, the lactic acid selectivity was 86.2% at the 1,2-propanediol conversion of 96.2% over Pd2/HAP-6 catalyst while the lactic acid selectivity was 88.8% at the 1,2-propanediol conversion of 86.3% over Pd1Ag1/HAP catalyst. The activation energies for the catalytic oxidation of 1,2-propanediol were in the order of Ea (Pd1Ag1/HAP) < Ea (Pd2/HAP-6) < Ea Ag2/HAP.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...