New 13-pyridinealkyl berberine analogues intercalate to DNA and induce apoptosis in HepG2 and MCF-7 cells through ROS mediated p53 dependent pathway: biophysical, biochemical and molecular modeling studies†
Abstract
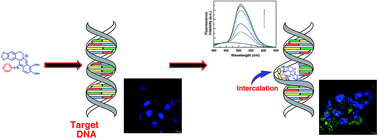
A new series of 13-pyridinealkyl berberine analogues was synthesized and their DNA binding efficacy studied by employing spectroscopic, calorimetric and molecular modeling techniques. Analogues with more than one CH2 group showed better intercalative binding than berberine. The analogue with one CH2 group bound DNA weaker than berberine. The binding of the analogue with single CH2 group was entropy driven, while those with more than one CH2 group was favoured by both entropy and enthalpy changes. Higher salt concentration and temperature destabilized the binding. A larger contribution from non-polyelectrolytic forces to the Gibbs energy and the involvement of strong hydrophobic interactions were inferred. Molecular modeling pin pointed the specific binding site and the non-covalent interactions in the association. The best DNA binding analogue (BER5) inhibited the growth of hepatocellular and breast carcinoma most efficiently. It induced apoptosis in HepG2 and MCF-7 cells with externalization of phosphatidylserine and reactive oxygen species generation with accumulation of cells in the G0/G1 phase. Furthermore, up regulation of p53 and p21 indicated the role of p53 in BER5 mediated apoptosis. The results suggested that 13-pyridinealkyl berberine analogues intercalated to DNA much stronger than berberine, the chain length of the linker plays an important role for the binding, and they induced ROS mediated apoptosis in HepG2 and MCF-7 cells by p53 modulation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...