Co-delivery of doxorubicin hydrochloride and verapamil hydrochloride by pH-sensitive polymersomes for the reversal of multidrug resistance†
Abstract
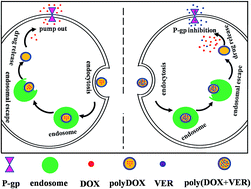
In this paper, we synthesized the pH-sensitive and biodegradable amphiphilic polypeptide-based block copolymer methoxy-poly(ethylene glycol)2K-poly(ε-caprolactone)4K-poly(glutamic acid)1K (mPEG2K-PCL4K-PGA1K). mPEG2K-PCL4K-PGA1K had low critical aggregation concentration and could self-assemble into polymersomes in aqueous solution revealed by transmission electron microscopy. Therefore, two hydrophilic drug doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX) and verapamil hydrochloride (VER) were encapsulated into the mPEG2K-PCL4K-PGA1K polymersomes to form poly(DOX + VER) co-delivery system to reverse the multidrug resistance by inhibiting the expression of P-glycoprotein and improve the anti-cancer effect of DOX. The in vitro cytotoxicity experiments indicated the obviously higher inhibition ratio to MCF-7/ADR resistant cells of poly(DOX + VER) compared with that of free DOX solution and polyDOX. The release rate of the two drugs from poly(DOX + VER) were much slower than that from the free drug solutions, and their release behaviors exhibited high pH-sensitive character. Furthermore, the low hemolysis ratio of mPEG2K-PCL4K-PGA1K confirmed that the copolymer could be applied for intravenous injection safely. Therefore, all these findings indicated that the co-delivery of DOX and VER by mPEG2K-PCL4K-PGA1K polymersomes is very promising for cancer therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...