Hydrophilic modification of ordered mesoporous carbon supported Fe nanoparticles with enhanced adsorption and heterogeneous Fenton-like oxidation performance
Abstract
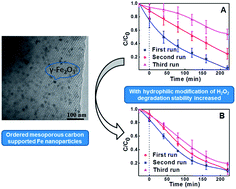
In this study, an ordered mesoporous carbon catalyst containing uniform iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe/meso-C) has been synthesized and underwent hydrophilic surface modification with hydrogen peroxide, which shows excellent adsorption and heterogeneous Fenton degradation performance for methylene blue (MB). Characterization using XRD, TEM, SEM, TG and N2 sorption–desorption isotherms showed that Fe/meso-C treated with hydrogen peroxide (H-Fe/meso-C) maintained a hexagonally arranged mesostructure, uniform mesopore size (∼2.3 nm), high surface area (up to 530 m2 g−1) and moderate pore volume (0.29 cm3 g−1) as an untreated catalyst. The Fe2O3 nanoparticles were highly dispersed in the carbon framework and mesopore channels. The hydrophilicity of the catalyst surface also improved after H2O2 modification. As a milder oxidizing agent, hydrogen peroxide was used to introduce the oxygen-containing group on the carbon surface. Due to the hydrophilic surface and retaining mesoporous structure, the H-Fe/meso-C catalyst presents a better Fenton-like catalytic performance than Fe/meso-C. The adsorption and heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation of MB reached 96% in 220 min with optimal oxidation conditions of 30 mg L−1 MB solution, 0.7 g L−1 catalyst, 50 mmol L−1 H2O2 and the initial pH value.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...