A naked-eye pH-modulated ratiometric photoluminescence sensor based on dual-emission quantum dot@silica nanoparticles for Zn2+ and IO3−†
Abstract
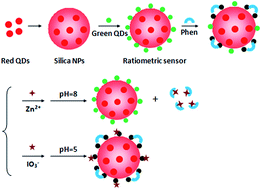
In this study, we report development of a ratiometric photoluminescence (PL) sensor comprising dual-emission quantum dots (QDs)@silica nanoparticles for the detection of Zn2+ and IO3−. The PL signal of the red-emitting QDs in the silica nanoparticles core worked as a reference, while the PL signal of the green-emitting QDs covalently linked onto the silica surface could be selectively quenched or restored by the analyte. After PL quenching of the green-emitting QDs by phenanthroline (Phen), Zn2+ can recover the PL under alkaline conditions via the formation of a Zn–Phen complex in the solution. Besides, IO3− can interact with the green-emitting QDs through oxidation–reduction reactions under acidic conditions, leading to further PL quenching. Under the optimized conditions, linear relationships between the PL intensity ratio of the ratiometric system and ion concentration were obtained from 5 to 100 μM for Zn2+ and from 5 to 150 μM for IO3−. The limits of detection (LOD) for Zn2+ and IO3− were 1.15 and 1.76 μM, respectively. The proposed method was sensitive, highly selective and intuitional. It has been successfully applied towards the determination of Zn2+ and IO3− in serum samples and table salt with satisfactory results.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...